Natalizumab
Description
This is a humanized IgG4 antibody using the same sequences as the therapeutic antibody natalizumab. It binds to the α4 subunit of α4β1 and α4β7 integrins, effectively blocking leukocyte adhesion mediated by α4 to their counter-receptors. By attaching to integrin, natalizumab is thought to stop white blood cells from entering the brain and spinal cord tissue, thereby mitigating inflammation and the resulting nerve damage. In vivo, natalizumab may further impede the interaction between α4-expressing leukocytes and their ligands in the extracellular matrix and on parenchymal cells, preventing recruitment and inflammatory activity of activated immune cells. The interaction of the endothelial receptor MAdCAM1 and the α4β7 integrin has been identified as an important contributor to chronic inflammation in Crohn’s disease (CD). MAdCAM1 is primarily expressed on gut endothelial cells and plays a crucial role in guiding T lymphocytes towards gut lymph tissue located in Peyer’s patches. Increased MAdCAM1 expression is frequently observed at active inflammation sites in CD patients, suggesting its involvement in recruiting leukocytes to mucosa. Consequently, natalizumab’s clinical effect on CD may be attributed to its ability to block molecular interactions between the α4β7 integrin and MAdCAM1 expressed on venular endothelium at inflammatory foci.
Product name | Natalizumab Biosimilar |
Species | Homo sapiens |
Expression system | CHO-K1 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | ELISA, assay, in vivo |
Aliases/Synonyms | Tysabri®, Antegren®, AN100226, AN100226M, BG00002 |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Isotype | IgG4 |
Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Biosimilar |
Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
Expression system | CHO-K1 |
Applications | Elisa, assay, in vivo |
| Amount | Price |
| 1mg | ¥1200 |
| 5mg | ¥3000 |
| 10mg | ¥5000 |
| 25mg | ¥7500 |
| 50mg | ¥10000 |
| 100mg | ¥14000 |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
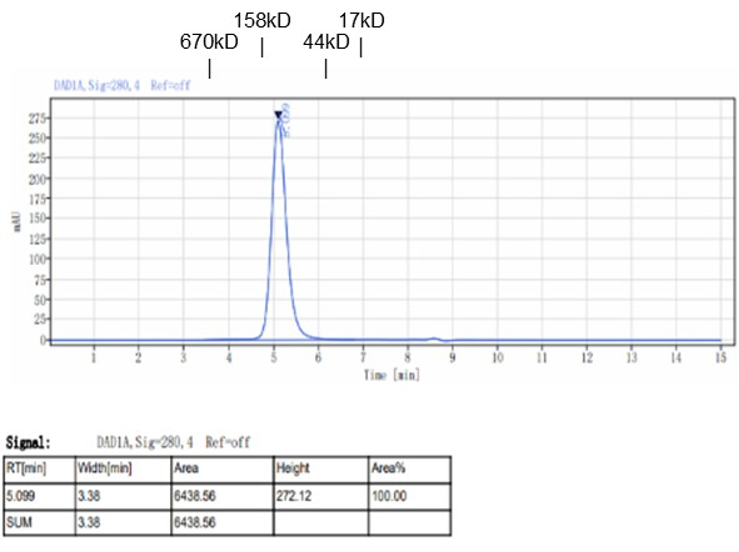
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
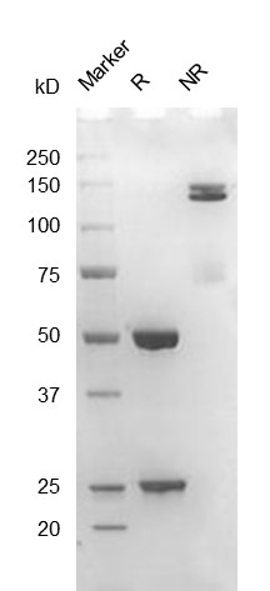
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4