Ranibizumab
Description
This is a humanized kappa Fab using the same sequences as the therapeutic antibody ranibizumab. It is a recombinant monoclonal antibody fragment specifically targeting human vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), which is a glycoprotein implicated in the pathophysiology of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Ranibizumab binds to VEGF-A with high affinity, including its biologically active forms such as VEGF165, VEGF121 and VEGF110. Notably, VEGF165 is the predominant isoform in the human eye that promotes ocular neovascularization. VEGF165 enhances vascular permeability, inhibits apoptosis, and causes endothelial-cell mobilization from the bone marrow and differentiation for angiogenesis. Ranibizumab binds to the receptor-binding site of VEGFA, preventing its interaction with its receptors – VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 – expressed on endothelial cell surfaces. Consequently, it attenuates endothelial cell proliferation, vascular leakage, and new blood vessel formation. Ranibizumab is used to treat various ocular disorders characterized by abnormal blood vessel growth like neovascular (wet) AMD. Its development first began after bevacizumab, another anti-VEGF anticancer drug, was discovered to inhibit neovascularization and used in the off-label treatment of neovascular AMD for intravenous injection. In order to improve drug delivery to the target organ, ranibizumab is available for intravitreal use.
Product name | Ranibizumab |
Species | Homo sapiens |
Expression system | CHO-K1 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | ELISA, assay, in vivo |
Aliases/Synonyms | Lucentis®, Susvimo™, Byooviz, Cimerli, Raivisio, Ranopto, rhuFab V2, RG-3645 |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Isotype | hKappa |
Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Biosimilar |
Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
Expression system | CHO-K1 |
Applications | Elisa, assay, in vivo |
| Amount | Price |
| 1mg | ¥1800 |
| 5mg | ¥3500 |
| 10mg | ¥6000 |
| 25mg | ¥9500 |
| 50mg | ¥12000 |
| 100mg | ¥18000 |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
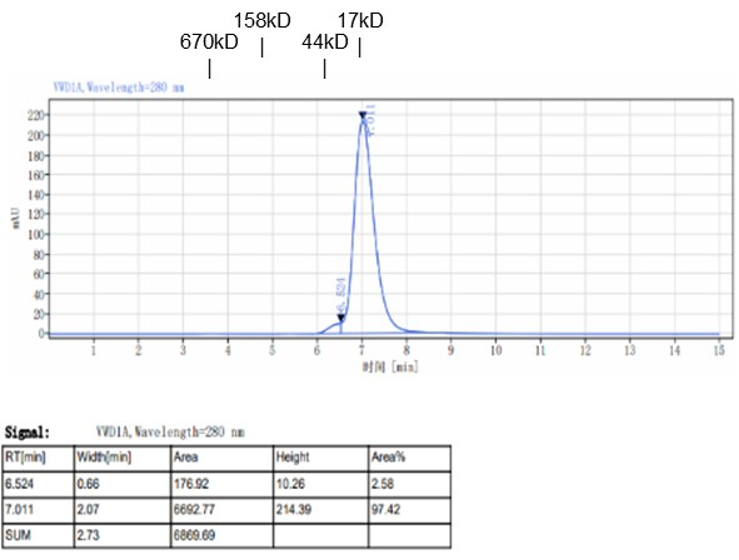
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
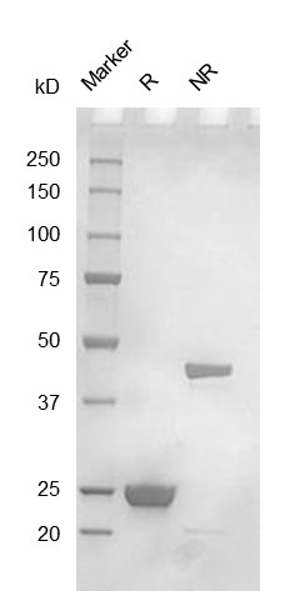
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4