hCD19(20-291)-His
Description
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 is a single-pass type I transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It consists of two Ig-like C2-type domains, and is expressed on follicular dendritic cells and B cells. CD19 acts as a co-receptor for the B-cell antigen receptor complex (BCR) on B-lymphocytes. It is required for mature B cell responsiveness to antigen stimulation, germinal center development, and antibody affinity maturation, but not necessary for early stages of B cell differentiation in the bone marrow. CD19 associates with various molecules including BCR, CD81, CD38, CD21, CD22, and IFITM1/CD225/Leu-13, to amplify B cell signaling and lower the threshold for antigen stimulation through the BCR. It initiates signaling pathways that lead to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation and intracellular Ca2+ store mobilization. CD19 polymorphisms and up-regulation can lead to the development of autoimmunity by promoting autoantibody production. Mutations in it are associated with severe immunodeficiency syndromes characterized by diminished antibody production. CD19 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target for hematologic cancers and solid tumors, such as leukemias and lymphomas. Immunotherapy utilizing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) directed against it has also gained significant attention.
Product name | hCD19(20-291)-His |
Species | Homo sapiens |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | Cancer Research, Immune Checkpoint, Immunotherapy, Targeted Therapy |
Aliases/Synonyms | B-lymphocyte surface antigen B4, B4, differentiation antigen CD19, T-cell surface antigen Leu-12, Leu-12, CVID3, MGC12802 |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Antigen |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Applications | Cancer Research, Immune Checkpoint, Immunotherapy, Targeted Therapy |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
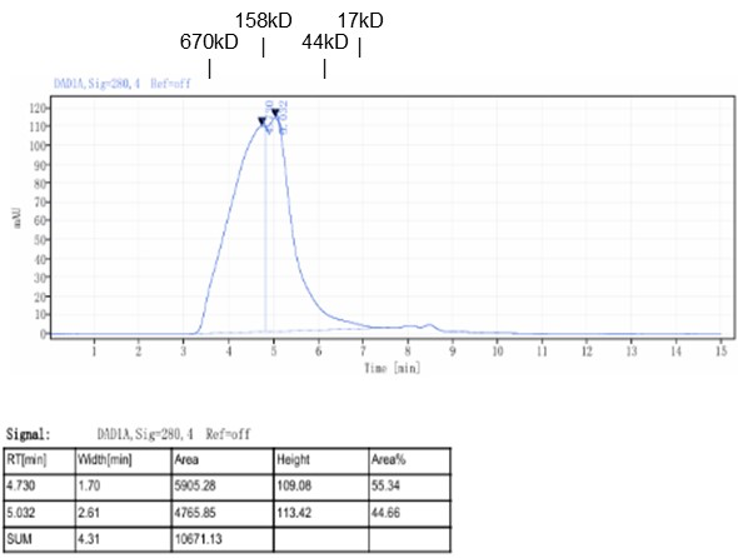
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
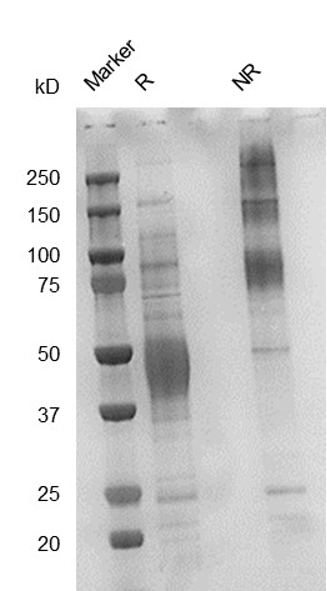
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4