hEGF(971-1023)-His
Description
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a potent growth factor that has the ability to induce cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. It stimulates the growth of various epidermal and epithelial tissues in vivo and in vitro, as well as some fibroblasts in cell culture. EGF is the founding member of the EGF family, which also includes TGF-alpha, amphiregulin (AR), betacellulin (BTC), epiregulin (EPR), heparin‑binding EGF‑like growth factor (HB‑EGF), epigen, and the neuregulins (NRG) -1 through -6. All EGF family members are synthesized as type I transmembrane precursor proteins that may contain several EGF domains in the extracellular region, and share highly similar structural and functional characteristics. The mature proteins are released from the cell surface by regulated proteolysis. Physiologically, EGF is found in various body fluids, such as blood, milk, urine, saliva, seminal fluid, pancreatic juice, cerebrospinal fluid, and amniotic fluid. EGF binding induces dimerization of the EGF receptor, leading to activation of the protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. These receptors undergo a complex pattern of ligand-induced homo- or hetero-dimerization to transduce EGF family signals. Subsequently, the tyrosine kinase activity initiates a signal transduction cascade that results in a variety of biochemical changes in the cell, including elevated intracellular calcium levels, increased glycolysis and protein synthesis, and upregulation of certain genes expression such as EGFR. Ultimately, these alterations lead to DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Biological activities ascribed to EGF encompass epithelial development, angiogenesis, healing of oral and gastroesophageal ulcers, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, fibroblast proliferation, and colony formation of epidermal cells in culture. Because of the increased risk of cancer development, inhibiting EGF can effectively mitigate this risk.
Product name | hEGF(971-1023)-His |
Species | Homo sapiens |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | Cancer Research, Diabetes/Weight Regulation, Inflammation Research, Immune System, Organoids, Stem Cells & Differentiation, Wound Healing |
Aliases/Synonyms | Urogastrone, beta-urogastrone, URG, HOMG4 |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Cytokine |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Applications | Cancer Research, Diabetes/Weight Regulation, Immune System, Inflammation Research, Organoids, Stem Cells & Differentiation, Wound Healing |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
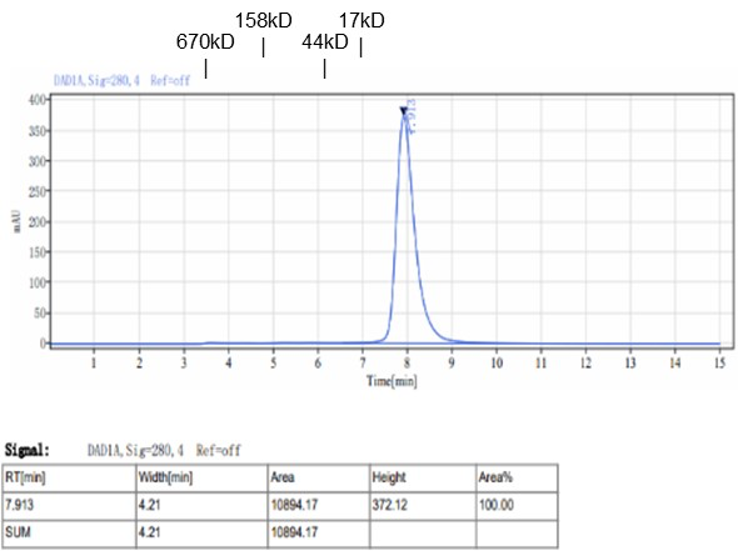
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
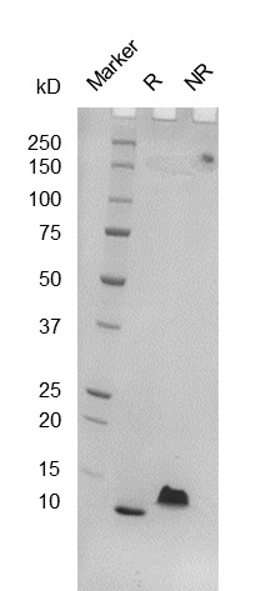
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4