hIL1b(117-269)-His
Description
Interleukin-1 beta (IL1b) is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine primarily synthesized by activated macrophages as a proprotein. It undergoes proteolytic processing to its active form by caspase 1 (CASP1/ICE). Initially discovered as the major endogenous pyrogen, IL1b induces prostaglandin synthesis, neutrophil influx and activation, T-cell activation and cytokine production, B-cell activation and antibody generation, as well as fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. Additionally, it promotes Th17 differentiation of T-cells. Furthermore, IL1b synergizes with IL12 to induce IFNG synthesis from Th1 cells. Moreover, it plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing VEGF production synergistically with TNF and IL6. Involved in transduction of inflammation downstream of pyroptosis: its mature form is specifically released into the extracellular milieu by passing through the gasdermin-D (GSDMD) pore. The induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (PTGS2/COX2) by this cytokine in the central nervous system (CNS) has been found to contribute to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Both IL1a and IL1b bind to the same receptor and exhibit similar but not identical biological properties. The mature human IL1b shares 96% amino acid sequence identity with rhesus while sharing 67-78% identity with canine, mouse and rat IL1b. This gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2.
Product name | hIL1b(117-269)-His |
Species | Homo sapiens |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | Cancer Research, Immune Checkpoint, Immunotherapy, Infectious Diseases, Neuroinflammation, Targeted Therapy |
Aliases/Synonyms | IL-1b, IL-1 beta, IL1F2, catabolin, lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF), endogenous pyrogen (EP), leukocyte endogenous mediator (LEM), mononuclear cell factor (MCF) |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Cytokine |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Applications | Cancer Research, Immune Checkpoint, Immunotherapy, Infectious Diseases, Neuroinflammation, Targeted Therapy |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
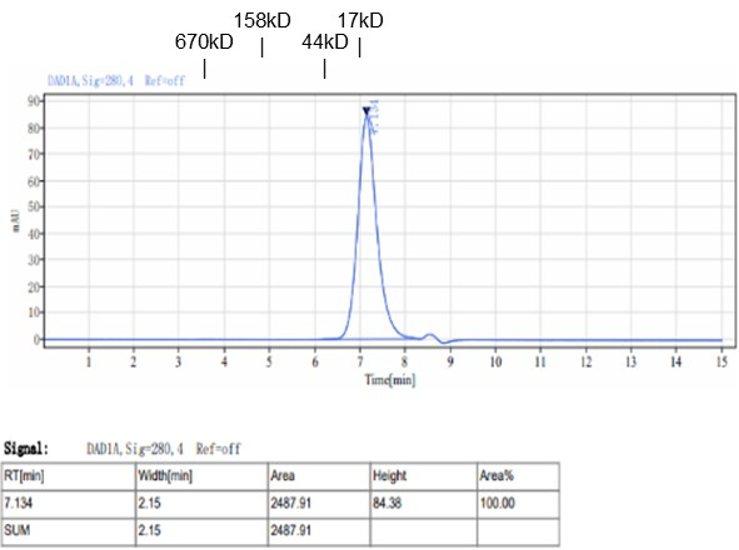
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
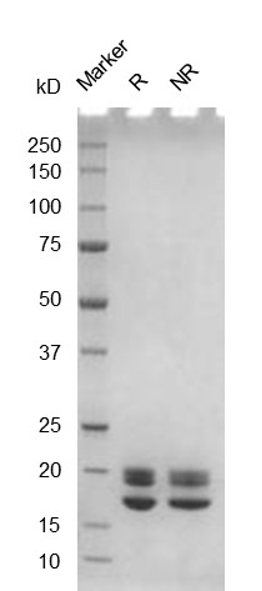
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4