hTNFa(77-233)-His
Description
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFa) is a cytokine that binds to TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. It is primarily secreted by monocytes and macrophages, exerting its ability to induce cell death of certain tumor cell lines. Under certain conditions, TNFa can stimulate cell proliferation and induce cell differentiation. It is potent pyrogen causing fever by direct action or by stimulation of IL1 secretion and is implicated in the induction of cachexia. TNFa exhibits apoptotic effects on cells, induces inflammation, inhibits tumorigenesis and viral replication. Thus, dysregulation of TNFa production has been associated with various human diseases, including major depression, Alzheimers disease and cancer. TNFa impairs the function of regulatory T-cells (Treg) in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis by dephosphorylating FOXP3, leading to its inactivation and functional defects in Treg cells. TNFa serves as a pivotal mediator of cell death in the anticancer action of BCG-stimulated neutrophils combined with DIABLO/SMAC mimetic in the RT4v6 bladder cancer cell line. TNFa induces insulin resistance in adipocytes by inhibiting insulin-induced IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation and glucose uptake. It triggers degradation of GKAP42 in adipocytes, contributing partially to TNF-induced insulin resistance. In terms of angiogenesis, TNFa synergistically induces VEGF production along with IL1b and IL6. TNFa promotes osteoclastogenesis and therefore mediates bone resorption. The TNFa intracellular domain (ICD) induces IL12 production in dendritic cells.
Product name | hTNFa(77-233)-His |
Species | Homo sapiens |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | Cancer Research, Diabetes, Immune Checkpoint, Immunotherapy, Inflammation Research, Neuroinflammation, Obesity, Targeted Therapy |
Aliases/Synonyms | TNF-a, TNF alpha, TNFSF2, Chchectin, Differentiation-inducing factor (DIF), APC1 Protein, Necrosin, Cytotoxin |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Cytokine |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Applications | Cancer Research, Diabetes, Immune Checkpoint, Immunotherapy, Inflammation Research, Neuroinflammation, Obesity, Targeted Therapy |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
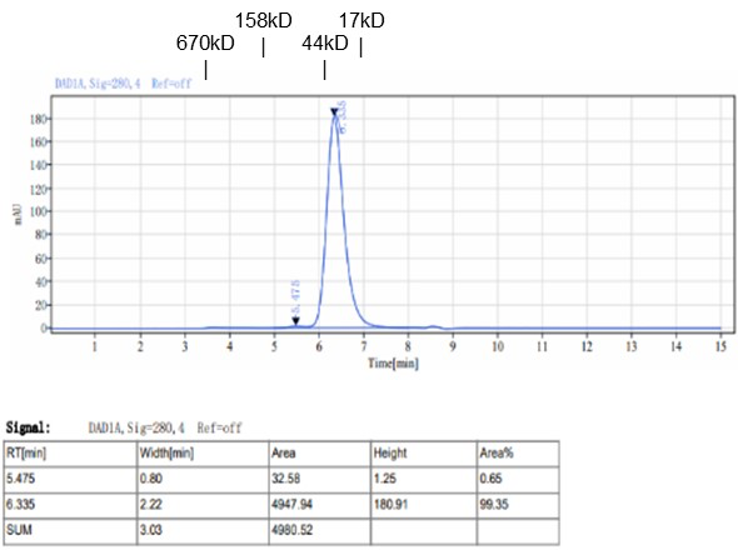
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
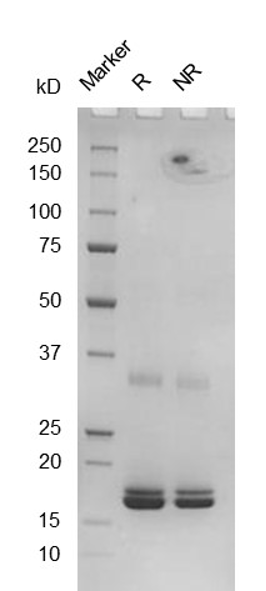
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4