mIL12b(23-335)-mIL23a(20-196)-His
Description
Interleukin 23 (IL23) is a proinflammatory, heterodimeric cytokine consisting of two disulfide-linked subunits, a unique p19 subunit, and a p40 subunit that is shared with IL12. It plays different roles in both innate and adaptive immunity. IL23 is released by antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells or macrophages. It binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12Rb1 and IL23R, activates JAK2 and TYK2 which subsequently phosphorylate the receptor to create a docking site leading to the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT4. This process triggers the activation of several pathways including p38 MAPK or NF-kappa-B, thereby promoting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL17a. By inducing autoimmune inflammation, IL23 may be implicated in autoimmune inflammatory diseases and tumorigenesis. It promotes the expansion and survival of Th17 cells, a CD4+ helper T-cell subset that produces IL17, as well as other IL17-producing cells. IL23 has biological activities that are similar to, but distinct from IL12. Both of them induce proliferation and IFNg production in NK cells. While IL12 acts on both naïve and memory human T cells, the effects of IL23 is limited to memory T cells.
Product name | mIL12b(23-335)-mIL23a(20-196)-His |
Species | Mus musculus |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | Allergy Research, Cancer Research, Immune System, Inflammation Research, Neurobiology Research |
Aliases/Synonyms | IL-23, p19, p40, SGRF, MGC79388 |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Cytokine |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Applications | Allergy Research, Cancer Research, Immune System, Inflammation Research, Neurobiology Research |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
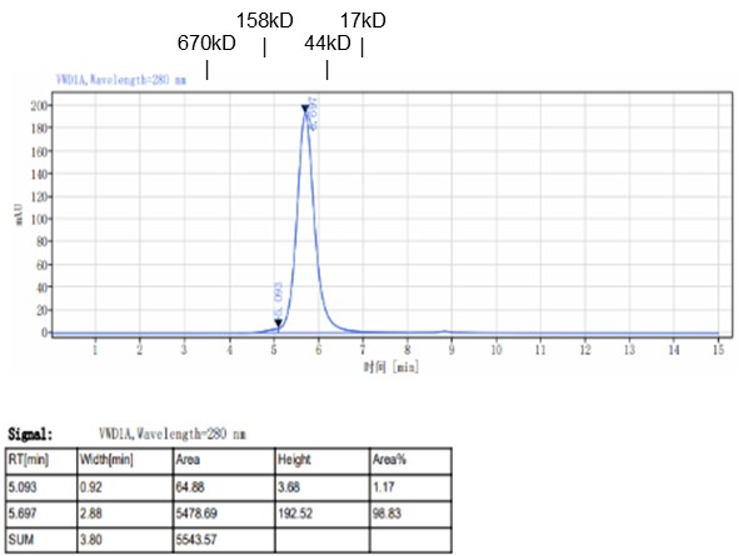
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
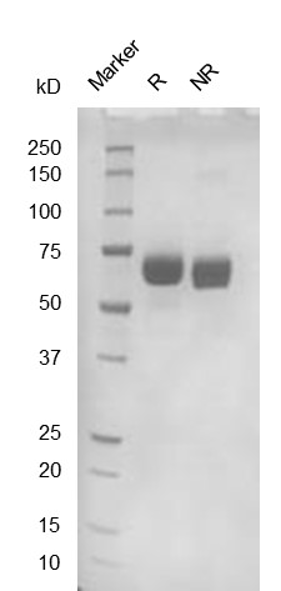
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4