mIL6(25-211)-His
Description
Interleukin-6 (IL6) is a multifunctional cytokine involved in various biological processes including immunity, inflammation, tissue regeneration, metabolism, and cancer progression. It acts as a potent inducer of the acute phase response. IL6 initiates signaling through a cell surface heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of the ligand binding subunit IL6Ra and the signal transducing subunit gp130. Upon binding to IL6Ra, it triggers IL6Ra association with gp130 and gp130 dimerization. This mechanism known as trans-signaling allows complexes of soluble IL6 and IL6Ra elicit responses from gp130-expressing cells that lack cell surface IL6Ra. Trans-signaling enables a broader range of cell types to respond to IL6, since the expression of gp130 is ubiquitous while that of IL6Ra is predominantly restricted to hepatocytes, monocytes, and resting lymphocytes. Rapid production of IL6 contributes to host defense during infection and tissue injury, but excessive synthesis is involved in disease pathology. In innate immune response, IL6 is synthesized by myeloid cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, upon recognition of pathogens through TLRs at infected sites or injured tissues. In adaptive immune response, IL6 is required for the differentiation of B cells into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Together with TNFa and IL1, IL6 drives the acute inflammatory response and the transition from acute inflammation towards either acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory disease. When dysregulated, it contributes to chronic inflammation in obesity, insulin resistance, inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, sepsis, and atherosclerosis. IL6 can also function as an anti-inflammatory molecule, as in skeletal muscle where it is secreted in response to exercise. In addition, it enhances hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and the differentiation of Th17 cells, memory B cells, and plasma cells.
Product name | mIL6(25-211)-His |
Species | Mus musculus |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 |
Delivery condition | Dry ice (-80°C) |
Delivery Time | 1 week if in stock; 4 weeks if production needed |
Storage condition | Store at -80°C |
Brand | BioMetas |
Applications | Allergy Research, Angiogenesis/Cardiovascular Research, Cancer Biomarkers, Cancer Research, Cell Culture, Diabetes/Weight Regulation, Immune Checkpoint, Immune System, Immunotherapy, Infectious Diseases, Inflammation Research, Neurobiology Research, Neuroinflammation, Obesity, Stem Cells & Differentiation, Targeted Therapy, Transplantation Research, Wound Healing |
Aliases/Synonyms | IL-6, B-cell differentiation factor, BCDF, B-cell stimulatory factor 2, BSF-2, BSF2, CTL differentiation factor, CDF, hybridoma growth factor, HPGF, HGF, HSF, interferon beta-2, IFN-beta-2, IFNB2, MGI-2, MGI-2A |
Reference | |
Note | For research use only. Not suitable for clinical or therapeutic use. |
Size | 1mg, 5mg, 10mg, 50mg, 100mg |
Brand | BioMetas |
Product type | Cytokine |
Expression system | HEK293 |
Applications | Allergy Research, Angiogenesis/Cardiovascular Research, Cancer Biomarkers, Cancer Research, Cell Culture, Diabetes/Weight Regulation, Immune Checkpoint, Immune System, Immunotherapy, Infectious Diseases, Inflammation Research, Neurobiology Research, Neuroinflammation, Obesity, Stem Cells & Differentiation, Targeted Therapy, Transplantation Research, Wound Healing |
Contact Us for a Quote!
Data Gallery
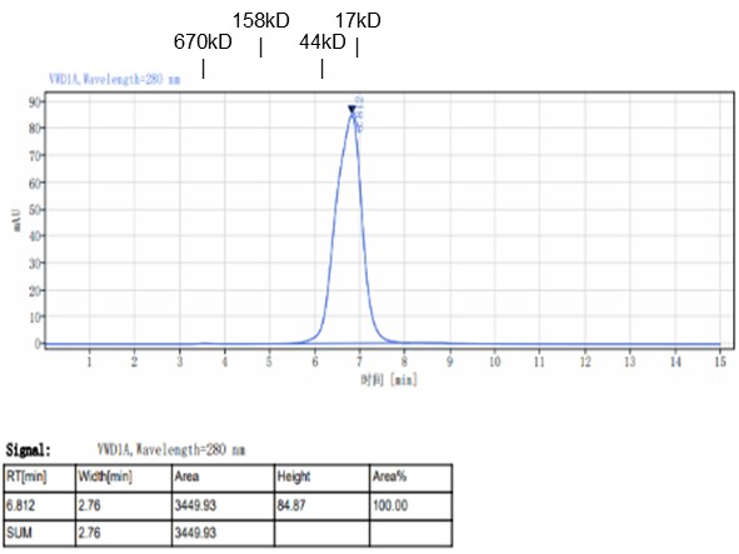
Fig. 1.) 4-20% SDS-PAGE analysis
Recombinant protein was visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining.
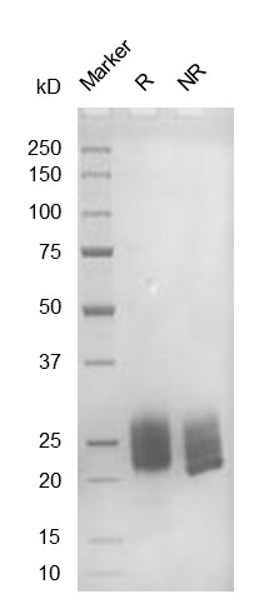
Fig. 2.) SEC-HPLC analysis
Column: Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL
Running buffer: 2xPBS, pH 7.4